https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.09921
Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning: Understanding and Perceiving Motion at Pixel Level
In this paper, we introduce Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning, a new motion understanding task that requires generating visual answers (video segmentation masks) according to the input question, and hence needs implicit spatiotemporal reasoning and grounding
arxiv.org
Abstract
- Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning task 제안
→ visual answer(video segmentation mask)를 generate하는 task이다. - 이 task를 수행하는 baseline model인 MoRA(Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning Assistant) 제안
Motivation

Fig. 1에서 conventional한 task들과 함께 새로 제안된 GroundMoRe Dataset이 visualize되어 있다. 질문은 총 네 종류(Causal, Sequential, Counterfactual, Descriptive)로 구성되어 있으며, 각각의 질문에 대한 정답은 pixel level의 spatiotemporal mask로 구성되어 있다.
Methods
Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning
Task Definition
input은 video clip $V\in ℝ^{t×h×w×3}$과 corresponding question $Q$이다. 이를 이용하여 정답인 binary object segmentation masks $M \in ℝ^{t'×h×w} (t'\le t)$를 return하면 된다.
이 task를 풀기 위해서는 motion-related reasoning과 pixel-level understanding을 수행해야 한다.
Video Collection
4개의 scenario에 대해서 720p YouTube video를 수집하였다: family, animal, ball game, outdoor activity; 이 중 temporal information 없이 문제 해결이 가능한 데이터는 제거했다. 전체 dataset specification은 Tab. 2에서 확인할 수 있다:

Q. RVS하고 다른 점이 정확히 뭐야?
→ Appendix A.4 참조해보면, 이전 MeViS dataset에도 비슷한 motion expression benchmark는 있었는데, 굳이 MGVR을 새로 정의한 것은, implicit reasoning을 추가했기 때문이라고 설명한다. 특히 MeViS에서는 input text에 identity leakage가 있다고 주장하며, 이를 증명하기 위해 MeViS의 object name을 something으로 변경한 후 실험하여 performance drop을 확인한다(Tab. 6 참조).

즉, target에 대한 직접적인 묘사를 피함으로써 model이 motion clue를 통해서 segmentation process를 진행할 수 있도록 한다.
Annotation Pipeline
15명의 CS student가 annotate했다. 이는 2-stage로 진행되었다:
Question Annotation Stage 1: Motion-related expression annotation
먼저 진행한 것은 motion-related expression annotation을 각 video에 대해 수행한 것이다. 세 type으로 expression annotation을 수행했는데, interaction-causal expression format은 <obj_A, motion, obj_B, before/after another motion>이고, interaction-temporal expression format은 <obj_A, motion, obj_B, before/after another motion>이다. 나머지는 descriptive expression인데, 여기서는 general dynamic scene description을 수행한다.
Question Annotation Stage 2: LLM-assisted QA generation
이를 이용하여 위에서 언급한 네 종류의 QA를 생성했다:
Causal question들은 interaction-causal expression으로부터 생성되었고,
Sequential, Counterfactual question은 interaction-temporal expression으로부터 생성되었다.
Descriptive question들은 descriptive expression으로부터 생성되었다.
이 example들은 Fig. 2, 13에서 볼 수 있고, Fig. 5, 6, 7에서 distribution을 확인할 수 있다:





question 자체는 GPT-4를 이용하여 생성되었고, annotator들이 manually check했다.
Experiments

여기서 제작한 방식은 MoRA(Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning Assistant)이라고 이름 붙여졌는데, 기본적으로는 LISA를 baseline으로 한다. 다만 LISA는 image segmentation을 위해 제작되었기 때문에 (LISA-2는 video도 되긴 한다), [LOC] token을 추가해서 temporal boundary information을 language space에 encode했다.
Results

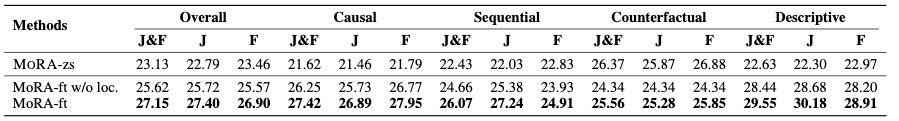
Jaccard index는 GT mask와 predicted mask의 IoU를 의미하고, F는 contour accuracy를 의미한다.
Tab. 3을 보면 MoRA가 SOTA임을 확인할 수 있다.

Tab. 4는 위에서 언급했던 implicit reasoning과 temporal context 관점에서 데이터를 분석한 것이다. GT를 제공할 경우 metric이 크게 개선되어 문제가 쉬워지는 것을 알 수 있다.
만약 temporal context만 제공한 경우 original clip의 temporal 정보만 활용하여 annotate했는데 1번째 row와 세 번째 row의 성능 차이가 크게 나는 것을 볼 수 있다.
→ implicit reasoning은 없을 경우 문제가 훨씬 쉬워진다.
Ablation study로는 temporal localization branch를 가지고 MoRA의 성능을 테스트했다. branch를 finetune하는 것이 꽤 중요하고, Descriptive question에서 특히 localization이 중요함을 확인할 수 있다.
Discussion
* 글쎄, contribution은 좀 모호하다. 이전 STVG task가 text 문장에서 reasoning이 필요하지 않다는 단점은 뚜렷한데, implicit하게 question을 바꿨다는게 task definition 자체를 바꿀 정도인지? + 모델은 그냥 LISA임.
* 다만 LLM 없이는 못 푸는 문제를 만들어냈다는 것은 좋은 점인듯.
* LISA 방식이 spatiotemporal mask를 만들 때 가장 좋은 방식인지? 이전 paper들 보면 cross attention등이 필요할 것 같은데
→ LISA 2 읽고 참조해볼 필요가 있어보임
References
Footnotes
'DL·ML > Paper' 카테고리의 다른 글
| VISA (ECCV 2024, RVOS) (0) | 2025.01.03 |
|---|---|
| VideoLISA (NeurIPS 2024,VOS) (1) | 2025.01.02 |
| VTP(EMNLP 2024, STVG) (0) | 2025.01.01 |
| CG-STVG(CVPR 2024) (1) | 2024.12.31 |
| Conditional MixLoRA (ACL 2024, MLLM PEFT) (0) | 2024.10.02 |