Video-LaVIT: Unified Video-Language Pre-training with Decoupled Visual-Motional Tokenization
Motivation

1. image encoder를 video encoding에 사용하는 것은 video의 spatiotemporal feature를 capture하는 데 적합하지 않음. 특히 temporal한 움직임들
2. 3d feature를 써서 둘을 capture하는 경우에는 video 자체의 redundancy 때문에 memory efficiency나 token length의 관점에서 효율적이지 않음
→ single key frame와 optical flow(motion vector)를 이용하여 video를 encoding하면 motion을 적은 cost로 잡아낼 수 있을 것
Methods
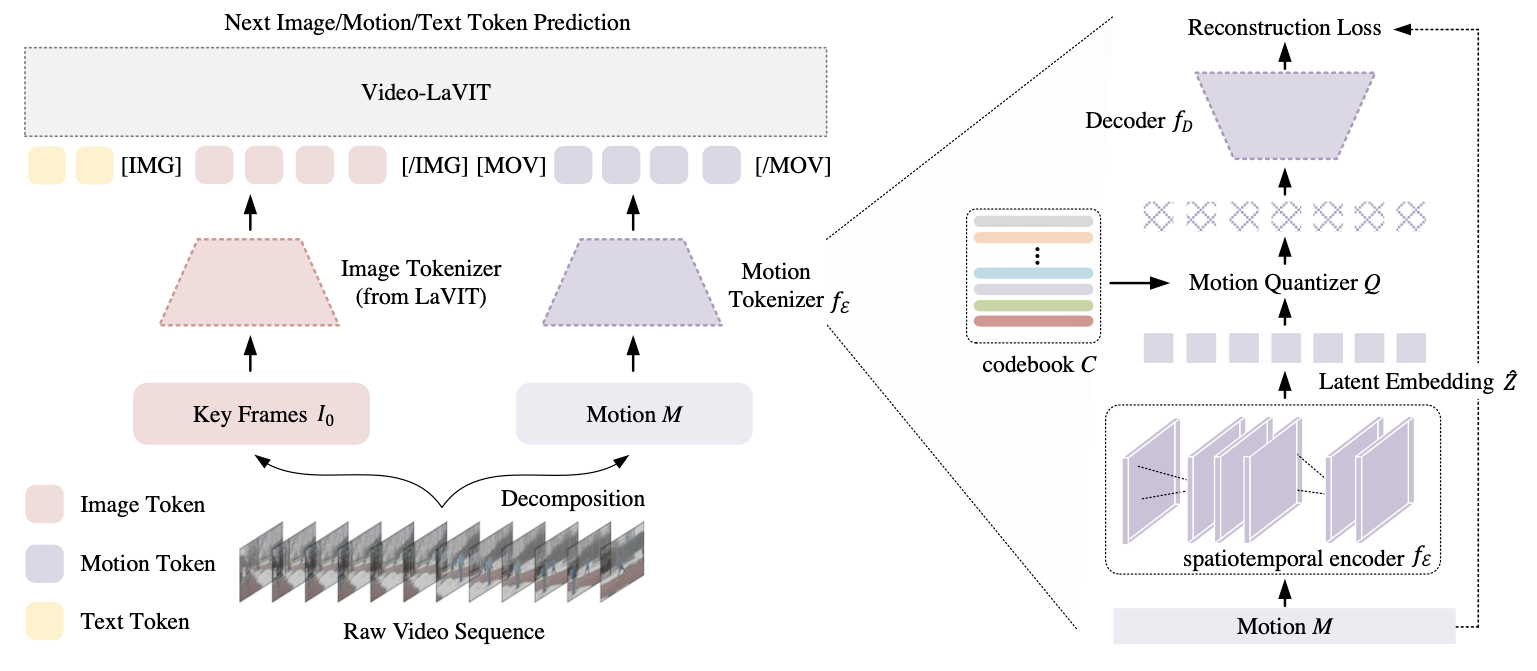
Video Tokenization
MPEG-4 format에서 I frame을 keyframe이라고 가정한다. 그 후 LaVIT[2] image tokenizer를 사용해서 keyframe을 tokenize한다. motion encoding에는 motion vector[3]를 사용한다.
→ keyframe 선정 방식은 이 work의 scope가 아니므로 임의로 설정된 방식이다.

motion vector는 encoding된 16*16 macroblock에서 adjacent한 두 개의 frame에 대해 corresponding block을 찾는 방식으로 구해진다(Eq. 1). 이로써 하나의 video clip은 key frame $I_0∈ℝ^{H×W×3}$과 motion vector $M∈ℝ^{T×{(H/16)}×{(W/16)}×2}$로 encode될 수 있는 것이다.
그 후 motion vector를 continous 1D vector로 mapping하기 위해서 VQ-VAE 구조의 encoder를 사용한다. 얻은 embedding vector $\hat z \in ℝ^d$는 L2 norm이 작은 codebook $c$로 quantized된다(eq. 2).

결과적으로 video는 $<visual, motion, \dots>$ code로 encode된다.
Video Detokenization

detokenization은 conditional U-Net을 이용한다. 종류는 두 가지로, keyframe U-Net과 video U-Net이 있다. keyframe U-Net은 visual token으로부터 reconstructed visual feature를 입력으로 받아 keyframe image를 reconstruct한다(fig. 3(b)).
video detokenizer의 경우에는 keyframe에 noise를 channel-wise로 concatenate한 것을 initial input으로 받아 motion vector를 condition으로 받는 3D U-Net이다. 이는 EDM training objectives로 train된다(eq. 3).

Long video의 경우에는 이 구조가 더 robust할 수 있음을 설명한다. noise를 이전 frame에서 DDIM $ΔT$만큼 reversed된 것을 사용한다(eq. 4). 이 경우 기존보다 spatial consistency를 더 잘 유지할 수 있다(fig. 5).


Experiments
Image/Video Understanding에 대해서만 확인한다.



Discussion
- 이런 형태로 video 외에 다른 modality를 추가해서 understanding 개선하는 것은 아주 좋은 방향인 것 같다
- 특히 optical flow를 써서 video를 압축하고 redundancy를 효과적으로 제거하는 것은 재밌는 방법이다
- 다만 trimmed video의 경우에는 optical flow가 계속 끊긴다. untrimmed video에 대해서만 적용할 수 있다는 점은 아쉽다
- 만약 untrimmed video에 대해서 적용하려면 끊기는 point → 단절되는 keypoint를 먼저 detection하고 그 안에서만 적용하면 될듯
- 다른 angle에서 촬영된 video들이 시간 순서대로 concate되어 있을 때 re-id할 수 있어야 할 것 같다
References
[1] Video-LaVIT: Unified Video-Language Pre-training with Decoupled Visual-Motional Tokenization
[2] Unified Language-Vision Pretraining in LLM with Dynamic Discrete Visual Tokenization
[3] Compressed video action recognition
Footnotes
'DL·ML > Paper' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CG-STVG(CVPR 2024) (1) | 2024.12.31 |
|---|---|
| Conditional MixLoRA (ACL 2024, MLLM PEFT) (0) | 2024.10.02 |
| UniHOI (NeurIPS 2023) (0) | 2024.09.24 |
| Co-DETR (ICCV 2023, OD) (0) | 2024.09.12 |
| IR Reasoner (CVPRW 2023, IR OD) (0) | 2024.08.30 |