Motivation
기존에도 Vision-Language model들을 Human-Object Interaction task에 사용하는 경우는 있었다.(PhraseHOI) 그러나 이 경우 다음과 같은 limitation이 있다:
- Limited Scalability: annotated data에 지나치게 의존하여 category가 limit된다.
- Suboptimal adaptability in zero-shot settings: HOI-VLM approach가 적은 word embedding category만 사용하여 그 adaptibility가 제한된다.
- task description에서 behavior를 추출하기 어렵다.
UniHOI에서는 VL model 대신 LLM을 이용하여 위의 limitation들을 해결하고자 한다.

Methods
Overview
기존 HOI task pipeline의 objective는 다음과 같다:

여기서 $\mathcal {I}$는 input images, $\mathcal{X}_\mathcal{I} = \{(\mathcal{I}_i)\}^{|\mathcal{X}|}_{i=1}$는 HOI dataset을 의미한다. 또한 $φ_{θ_\mathcal{D}}$는 $θ$로 parameterize되는 HOI detector를 의미한다. $\mathcal {Q}^{ho}$는 HOI pair related query이다.
이를 uniHOI에서는 다음과 같이 transform한다:

$φ_\mathcal{F}$가 생겼는데 이는 vision-language foundation model을 의미하고, 여기에 들어가는 것은 image $\mathcal{I}$, text $\mathcal {T}$ (구체적으로는 phrase annotation in $\mathcal{I_i}$), HOI specific prompt $\mathcal{P}^{ho}$이다.

HO Spatial Prompts Generation
Fig. 2와 같이 image를 CNN-based image encoder에 넣어 feature extraction한다. 얻어진 feature map은 projection하고 flatten하여 segment patch embedding을 얻는다.
이 patch embedding은 다시 project되어 positional encoding과 더해진 후 instance detection의 input이 된다.

이후 transformer encoder로 self-attention한다. 여기까지가 Fig. 2의 연두색 부분이다.
instance-level feature learning은 Fig. 2의 분홍색 부분에서 나타난다. instance decoder를 두어 human bbox와 object boxes, coategories를 locate한다.

Equation 4에서 볼 수 있듯이 prompt는 human box에 대한 prompt와 object boxes에 대한 prompt로 나뉜다. 이는 human query와 object query를 넣어서 만드는데, 이떄 position guided embedding $\mathcal{Q}^g$[2]을 더해서 만들게 된다.

여기에 FFN을 붙여서 바로 human bbox, object bbox, object categories를 detect할 수 있다.
이 방법으로 각각의 prompt가 bbox feature를 포함하도록 learning할 수 있다.
Prompt Foundation Models for HOI Modeling
BLIP2를 써서 HOI recognition을 수행한다. input image $\mathcal{I}$를 downsample 하여 얻은 $\mathcal{I}'$을 image encoder에 넣고 Q-former를 통해 feature extraction한다.

이렇게 얻은 image feature를 HO pair과 연결하기 위해 prompt를 입력으로 받는 HO decoder인 HO Prompt-guided Decoder(HOPD) $φ_{θ_{\mathcal{P}}}$를 사용한다.

여기서 $\mathcal{V}^f$는 HO pair와 correspond하는 high-level information을 의미한다.

Knowledge Retrieval for HOI Reasoning in Open World
원래는 HOI detection에서 word embedding만 사용하는데 이는 정보를 담기에 충분하지 않다. 이를 해결하기 위해 phrase description을 enrich하는데, 이때 GPT를 Knowledge Base로 사용하였다. 즉, phrase description $T^i$를 exapnd하여 more comprehensive knowledge description $\mathcal{K}^i$를 얻었다.
여기에 추가로 LLM의 knowledge retrieval process를 위해 `Knowledge retreive for verb_objection, limited to N words`로 rpompt를 주어 interaction category를 describe하게 하였다. 다음은 그 결과 예시이다.
- Riding a bicycle involves balance, coordination, and physical exertion. The rider mounts the bike, propels forward by pushing pedals with their feet. Steering is achieved by turning handlebars. Brakes slow or stop the bike. Helmets are worn for safety.
- Throwing a frisbee involves grasping the disc, typically with a forehand grip, then swinging the arm and releasing the frisbee at the right moment for it to glide through the air. Direction and distance depend on the angle and speed of the throw. It’s a common recreational activity.
to sum up
정리해보면, 먼저 HO spatial prompt를 만들기 위해 train하고,
text interaction에서 GPT로 expand한 다음에 이걸 BLIP으로 text feature extract한다. 으기로 image를 vision module에 넣어서 decoder 통과시켜서 HO feature를 얻은 다음에 text feature하고 similairity 계산해서 결과를 얻는다.
결과적으로 contribution이라고 할 것은 interaction의 description을 expand한 것, HO spatial prompt를 만든 것이다.
두 방법 정말 좋은 방법으로 생각되는게.. action recognition할 때 특정 action의 verb만 가지고는 내가 원하는 그림을 model이 이해하는지 확신하기가 어렵다는 것.
두 번쨰로는 spatial embedding이 약한 모델들에서 미리 확실하게 box coordinate에 대한 정보를 먹일 수 있다는 점이다.
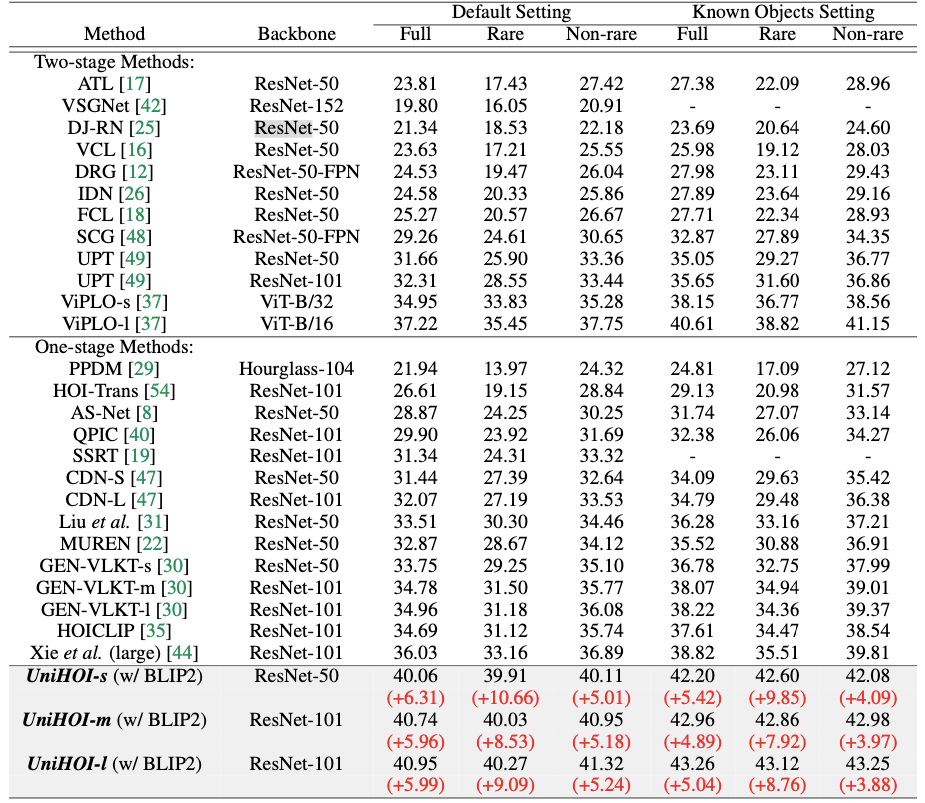
Experiments

Results
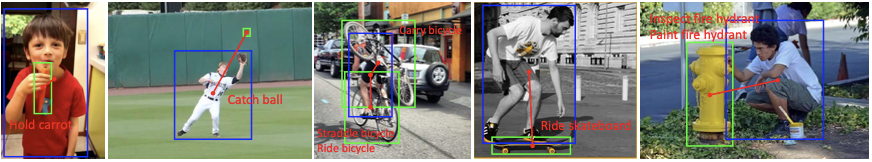
Discussion
References
[2] Liao, Y., Zhang, A., Lu, M., Wang, Y., Li, X., Liu, S.: Gen-vlkt: Simplify association and enhance interaction understanding for hoi detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 20123–20132 (2022)
Footnotes
'DL·ML > Paper' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Conditional MixLoRA (ACL 2024, MLLM PEFT) (0) | 2024.10.02 |
|---|---|
| Video-LaVIT (ICML 2024 Oral, Video tokenization) (0) | 2024.09.30 |
| Co-DETR (ICCV 2023, OD) (0) | 2024.09.12 |
| IR Reasoner (CVPRW 2023, IR OD) (0) | 2024.08.30 |
| LLVIP(IR dataset, ICCV 2021) (0) | 2024.08.30 |