Abstract
- X-VARS(EXplainable Video Assistant Referee System) 제안
- SoccerNet-XFoul -- 22k VQA question triplet about refereeing question benchmark 제안
Motivation
VAR system에서 explainability가 중요한 것은, 공식 경기의 판정 결과는 각 팀의 운명을 좌우할 수 있기 때문이다. 따라서 X-VARS는 LLM을 이용하여 automatic VAR의 explainability를 조명한다.

X-VARS LLaVa를 사용하는 VLM을 활용한다. vision encoder로는 CLIP ViT-L/14를 활용한다. 22k개의 video QA triplet을 포함한 SoccerNet-XFoul datsaet에 확인해보았으며, SoccerNet-MVFoul dataset에서 X-VARS는 SOTA를 달성했다.
SoccerNet-XFoul dataset

SoccerNet-XFoul dataset은 soccer 장면의 video-text pair를 10k video clip과 22k question으로 구성하였다. 이는 70명 이상의 노련한 referee들에 의해서 annotate되었다.
Questions
4개의 question으로 구성된다:
- "Is it a foul or not? Why?"
- "What card would you give? Why?"
- "the defender stops a promising attack or a goal-scoring opportunity?"
- "the referee could have give an advantage?"
이는 경기를 다각적으로 분석하고 이해해하며 미래를 예측할 수 있어야 답변이 가능한 질문이다.
Annotators
70명의 referee에게서 각자의 언어로 annotate된 뒤 ChatGPT-3.5를 이용하여 English로 translate되었다. 그 후 accurate translation인지 다른 referee에 의해 review되었다.
Subjectivity
Fig. 1에서 볼 수 있는 것처럼 referee마다 판단이 다를 수 있다. 따라서 각 question에 대해서 multiple answer를 구했다. 결과적으로는 각 question에 대해 1.5개의 answer이 존재하게 되었다.
Statistics

Fig. 2에서 common wods의 distribution을 보여준다. 대부분 두 player 간 경합을 묘사하는 terminology인 것을 볼 수 있다. 각 답변은 1 word에서 66 words 사이로 구성되었으며 평균적으로는 25 words로 inbalance하다.
X-VARS
Architecture

구조는 Video-ChatGPT의 구조를 그대로 활용한다. input의 크기는 $v∈ℝ^{T×H×W×C}$이고, 이를 CLIP ViT-L/14로 encoding한다.
CLIP encoder로 얻은 frame feature vector $f$와 hidden state $h$를 이용하여 temporal pooling과 spatial pooling을 수행한다. $h$를 pooling한 것을 각각 $s, t$ vector라고 하고 이를 concate하여 spatiotemporal feature를 얻는다.
$$z = [t s] ∈ℝ^{(S+T)×D_2}$$
이를 linear projection하여 visual toekn을 얻는다.
$$ w = Linear(z) \in ℝ^{(S+T)×D_2}$$
여기에 $f$도 temporal dimension으로 pooling하여 classification head에서 foul과 severity를 classification하게 된다. 이 class는 VARS를 따른다. (https://jordano-jackson.tistory.com/125 참조)
Label은 classification head의 argmax를 이용해 구했다:
$$P_{foul} =\arg \max C_{foul}$$
$$P_{sev} =\arg \max C_{sev}$$
이를 통해 얻어진 label은 LLM에 text prompt로 함께 입력되었다.
→ 물론 classification result하고 prediction하고 align되는 건 좋긴 한데.. LLM 안 거치고 classification을 하는게 BA가 낮아서 오히려 LLM의 성능을 저해할 수 있을 것 같다. 내 생각에는 LLM으로 class prediction을 하는게 더 좋을 듯.
LLM에 들어가는 prompt는 다음과 같은 형태이다:
$$\begin{align}&USER:<Question><P_{foul}><P_{sev}><w>\\&Assistant: \end{align}$$
Training
two-stage로 training한다. 먼저 CLIP을 multi-task classification에 finetune한다. 두 번째 step에서는 projection layer과 LLM의 몇 layer를 fine-tune해서 sport-specific domain에 fit하게 만든다.
Stage 1: Fine-tuning to inject football knowledge
CLIP을 SoccerNet-MVFoul dataset에 train했다.
Stage 2: Feature alignment and end-to-end training
CLIP을 freeze하고 linear layer와 LLM을 finetune했다. 이때는 Video-ChatGPT의 pretrained weight를 사용했다. training을 위해서는 QLoRA를 사용하였고 1%의 layer를 3 epoch으로 train했다.

Results
Human study on explananation performance
기존의 NLP metric은 대부분의 용어가 비슷하게 사용되는 이 task에서는 사용되기 어렵기 때문에 human evaluation을 사용했다. 20명의 referee에게 X-VARS인지 human referee에서 만들어진 것인지 알지 못하게 한 후에 20개의 random video clip을 각 5초간 여러 번 시청 후 explanation의 quality를 evaluate했다.
먼저 decision과 explanation이 Laws of the Game과 align하는지를 1(strongly disagree)부터 5(strongly agree)까지로 평가했다. 결과는 X-VARS가 human referee와 비슷하게 평가하였고 46%의 case에서는 human referee보다 convincing하였다. 반면 X-VARS는 disagree를 human referee보다 많이 받았다. 이는 주로 dataset의 lack 때문인 것으로 평가한다. 전체 결과는 Tab. 3에서 확인할 수 있다.
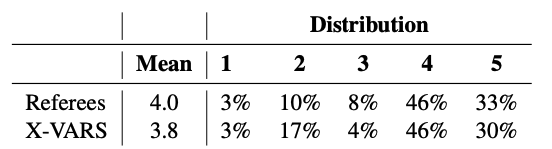
→ 다만 이건 balanced accuracy로 평가해야 할 소지가 있다.
Qualitative results

원래 Vicuna가 conversation이 가능하기 때문에 학습한 prompt 이외에도 대답을 잘 하는 것을 볼 수 있다. 다만 존재하지 않는 action에 대해 말하는 등의 hallucination problem에 대한 해결이 필요하다고 언급되었다.
Ablation Study
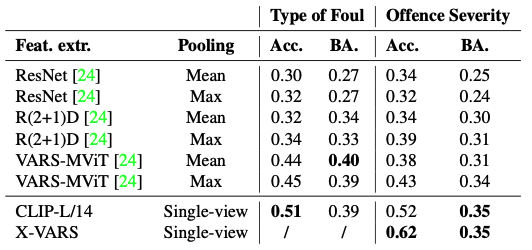
- Table 4는 VARS와의 비교를 보여준다. 다만 text로 generation되고 foul의 type에 대해서는 직접적으로 언급하지 않으므로 foul에 대해서는 classification할 수 없었다.
- 언제나 CLIP prediction과 LLM output이 일치하는 것은 아니었고 76%의 경우에만 agree했다.
- 주로 CLIP prediction이 있는 경우 성능이 더 잘 나왔다.
References
[1] Held, J., Itani, H., Cioppa, A., Giancola, S., Ghanem, B., & Van Droogenbroeck, M. (2024). X-vars: Introducing explainability in football refereeing with multi-modal large language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 3267-3279).
Footnotes
'DL·ML > Paper' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LLaVA (NeurIPS 2023 Oral, MLLM) (0) | 2024.07.10 |
|---|---|
| UniControl (NeurIPS 2023, Diffusion) (1) | 2024.07.08 |
| BASNet (CVPR 2019, OD) (0) | 2024.06.14 |
| DDPM (NeurIPS 2020, Diffusion) (1) | 2024.06.11 |
| VideoChat2 (CVPR 2024, MLLM) (0) | 2024.05.28 |